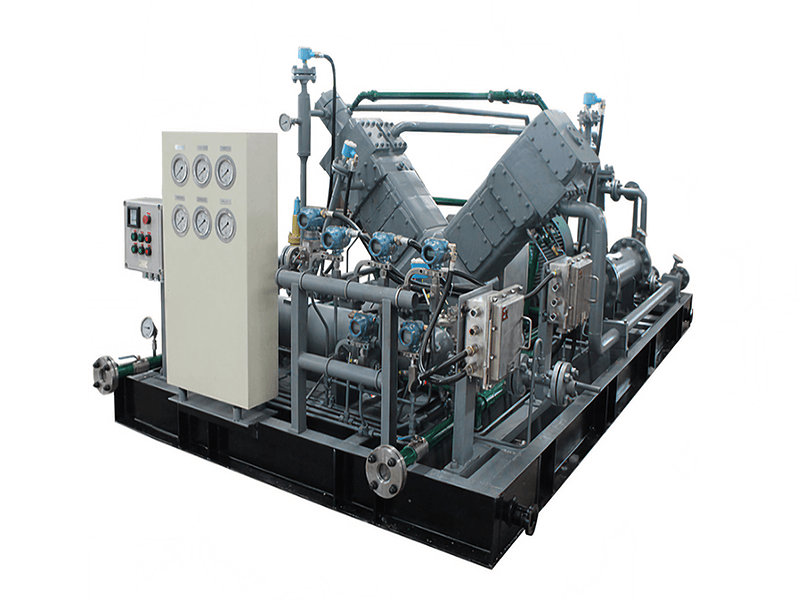
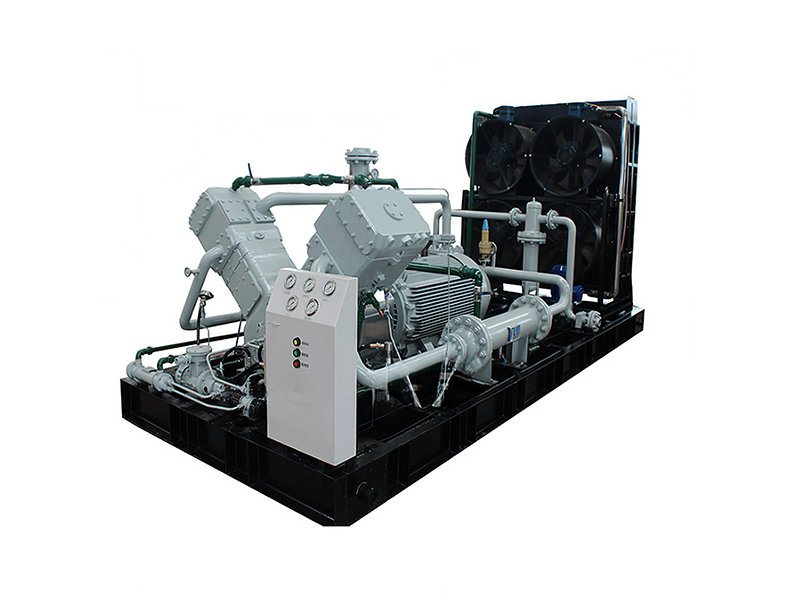
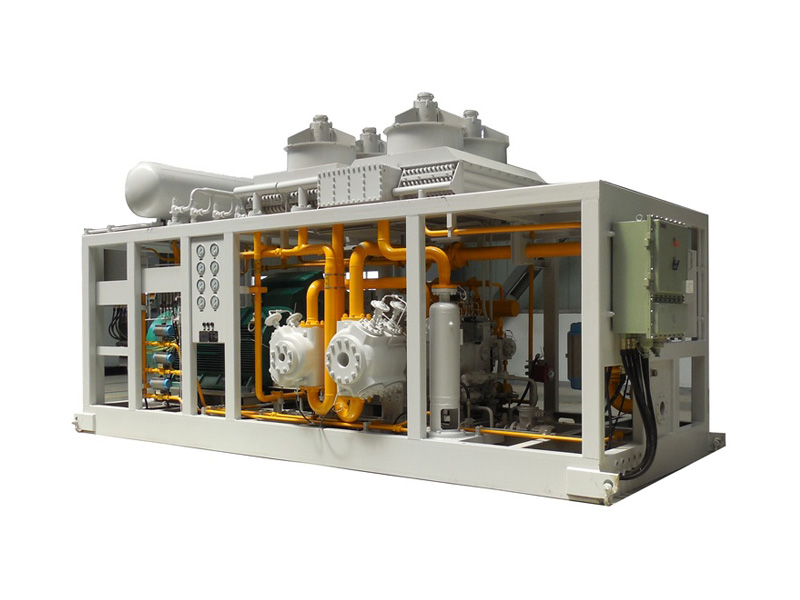
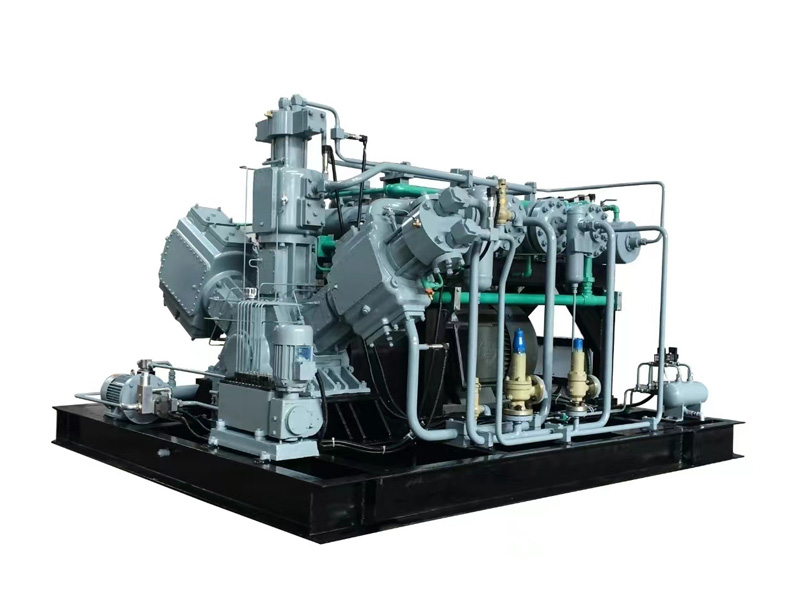
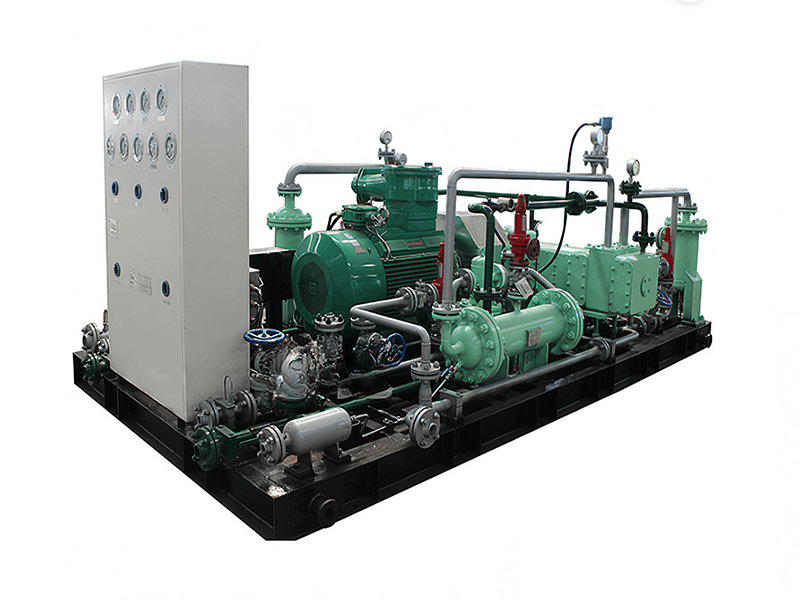
Helium compressors must meet a series of special technical requirements during their design and manufacturing processes. These requirements stem from the unique physical properties of helium and the demanding conditions of their application scenarios. The following outlines several key technical challenges and their corresponding solutions. These solutions must consider not only technical feasibility but also economic viability and reliability, ensuring stable equipment operation under various working conditions.
Leakage control is the primary technical challenge for helium compressors. Due to the extremely small molecular diameter and low viscosity of helium, traditional sealing methods are often inadequate. The most effective current solution is the use of non-contact sealing technologies. Dry gas seals introduce seal gas at a pressure higher than the process gas pressure on the sealed gas side, forming a gas film barrier against leakage, achieving a leakage rate of <1 ml/min. In practical applications, the seal gas pressure typically needs to be 0.15-0.25 MPa higher than the process gas pressure and must be equipped with a precise pressure regulation system. Magnetic fluid seals utilize the positioning characteristics of magnetic nanofluids in a gradient magnetic field to form multi-stage sealing barriers, achieving leakage rates on the order of 10⁻⁹ Pa·m³/s. This sealing method is particularly suitable for high-speed applications, but its pressure resistance is relatively limited, usually applicable for pressure differentials less than 2 MPa. Furthermore, all static seal interfaces must use metal gaskets or welded connections, avoiding the use of elastic seals. For flange connections, a double-ferrule structure combined with metal spiral wound gaskets is recommended to ensure sealing reliability.

Thermal management is another key technical difficulty. The high thermal conductivity and low specific heat capacity of helium complicate the control of temperature rise during compression. Effective solutions include: adopting multi-stage compression with intercooling, controlling the compression ratio per stage between 2.5-3.5; using efficient plate-fin heat exchangers as intercoolers, whose compact design can provide heat transfer coefficients as high as 5000 W/m²·K; employing special thermal oils as cooling media in high-temperature sections, with an operating temperature range from -60°C to 300°C; for high-power compressors, configuring forced circulation cooling systems to ensure heat dissipation effectiveness. In practical engineering, control strategies for the cooling system must also be considered, typically using PID control algorithms to regulate the cooling medium flow in real-time based on discharge temperature, keeping temperature fluctuations within ±2°C. Simultaneously, temperature protection devices must be installed to automatically take protective actions when temperatures exceed set values.
Material selection must consider the special behavior of helium under high pressure. At pressures exceeding 10 MPa, helium may permeate into the metal lattice, causing changes in material properties. Solutions include: selecting austenitic stainless steel 316L or duplex steel 2205 as the main body materials, as their dense grain structure can effectively block helium permeation; applying surface modification treatments to high-pressure components, such as nitriding or tungsten carbide spraying, to form a barrier layer; using nickel-based alloys 625 or 718 under extreme conditions, as their fracture toughness at low temperatures is superior to ordinary stainless steels. The influence of the coefficient of thermal expansion must also be considered during material selection to ensure dimensional stability of components during temperature changes. For moving parts, special surface treatments, such as chrome plating or nitriding, are required to improve wear resistance and galling resistance.
Vibration control is particularly important for helium compressors. The high speed of sound in helium can easily induce flow-excited vibrations. Effective control measures include: using rotor dynamics analysis to optimize bearing span and critical speeds, ensuring the operating speed avoids resonance regions; utilizing tilting pad bearings or magnetic bearings to provide better damping characteristics; avoiding sudden cross-sectional changes in flow path design, adopting gradual contours to reduce vortex generation; installing online vibration monitoring systems to monitor bearing vibration and shaft displacement in real-time. For vibration control, the vibration characteristics of piping must also be considered, with rational arrangement of pipe supports and vibration dampers. For high-speed compressors, modal analysis is recommended to ensure the system's natural frequencies are away from excitation frequencies.
Intelligent control systems represent the development trend for modern helium compressors. A complete control system should include: adaptive seal gas pressure regulation, automatically adjusting seal gas supply based on process pressure changes; intelligent temperature management, optimizing cooling system operation through fuzzy control algorithms; predictive maintenance functions, forecasting equipment status based on operational data trend analysis; remote monitoring and diagnostics, supporting cloud data analysis and expert system diagnosis. These functions are implemented via PLC or DCS systems and integrated with plant management systems. Modern intelligent control systems should also possess self-learning capabilities, continuously optimizing control parameters based on historical operational data to improve system efficiency. Simultaneously, the system must have comprehensive alarm and protection functions to ensure safe shutdown under abnormal conditions.
Beyond the key technologies mentioned above, helium compressors require special attention to system cleanliness control. As helium applications typically demand extremely high purity, the system interior must be kept highly clean. This necessitates strict cleaning processes during manufacturing, including component cleaning, pipeline purging, and system purification. During operation and maintenance, regular purity testing and system purification are required to ensure gas quality meets requirements. Furthermore, maintainability design must be considered, with critical components being easily accessible for inspection and replacement to reduce maintenance downtime.
In terms of energy efficiency optimization, modern helium compressors often use variable frequency drive (VFD) technology to automatically adjust operating status based on actual load, achieving energy-efficient operation. Concurrently, overall unit efficiency is improved by optimizing system design and operational parameters. For example, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis optimizes flow path design to reduce flow losses; thermodynamic analysis optimizes interstage pressure and temperature parameters to improve thermodynamic perfection. These measures can effectively reduce operating costs and enhance the economic performance of the equipment.
With continuous technological development, helium compressors are evolving towards higher efficiency, greater reliability, and increased intelligence. The application of new materials, adoption of new processes, and advancements in intelligent control technology will continuously drive improvements in the technical level of helium compressors. In the future, helium compressors will play an important role in more fields, providing strong support for technological progress and industrial development.